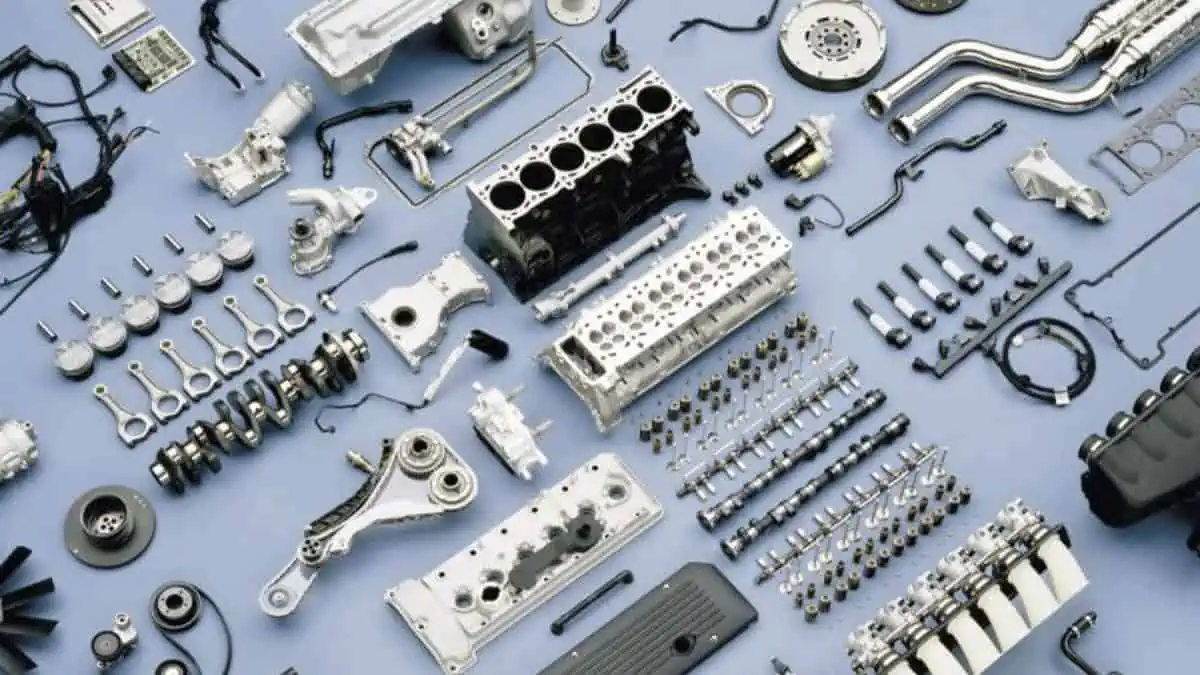
Have you ever wondered how the different car engine parts work as soon as you turn on the ignition? Your car’s engine is a complex system that is responsible for the vehicle’s operation. This guide covers the basic parts that are in every car’s engine.
Engine Structure
Engine Block
Also known as a cylinder block, the engine block provides structure to the overall system. All the necessary engine functions occur inside this block, such as:
- Intake
- Suction
- Combustion
- Compression
- Exhaust
The engine block has multiple holes to contain anywhere from four to twelve cylinders, depending on the car’s design.
Cylinder Head
Cylinder heads contain several other car engine parts, including a spark plug, combustion chamber, and exhaust valve. It prohibits air and gas from both entering and leaving the engine system, with a design made from either cast iron or aluminum.
Internal Engine Components
Piston
The piston is one of the most essential car engine parts. Made of either aluminum alloy or cast iron, the piston rotates within the car’s cylinder to convert the pressure energy from fuel combustion into vehicle power. From there, the power transmits to other parts of the engine.
Pistons can rise and fall within a cylinder as much as 2,500 times per minute.
Piston Rings
The piston features grooved rings around the diameter. Piston rings are vital to limit friction and seal off the space between the piston and the cylinder. Their many useful functions include:
- Sealing the combustion chamber to prevent gas leaks
- Keeping the right amount of oil between the piston and cylinder wall
- Improving the heat transfer
- Returning scraped oil to the oil pan
Crankshaft
A crankshaft receives the power that rotating pistons generate. It duplicates the pistons’ motion through the use of a crank lever and the connecting rod. This piece connects to the car’s flywheel to continue the process of operating the vehicle.
Camshaft
Located either on the engine block or the cylinder heads, the camshaft works in conjunction with the crankshaft. It takes the rotating motion of the crankshaft and converts it into an up-and-down motion.
This piece helps control the movement of other car engine parts, including the pushrods, valves, and lifters. It can also control the timing of the valve’s opening and closing.
Bearing
A bearing helps the car engine with three primary functions:
- Supporting machine elements
- Reducing friction
- Bearing thrust loads
This device is crucial for providing movement without losing power from friction.
Engine Valves And Timing
Engine Valves
The engine valves are other mechanisms that focus on the car’s air-fuel mixture and exhaust gases to run properly. They work by regulating the timing for when air enters and escapes the car’s cylinders.
When engine valves are open, air can flow in and out of the cylinder and combustion chamber. They will shut tightly from the pressure within the combustion chamber.
Intake And Exhaust Valves
These essential car engine parts appear within the cylinder head or walls. They take the energy charge from the air and fuel mixture within the combustion chamber and release it into the engine’s cylinder.
Timing Belt
A timing belt helps synchronize the rotation of the camshaft and crankshaft and therefore, controls the opening and closing of an engine’s valves.
Fuel And Combustion System
Carburetor
Gas engines need carburetors to atomize the fuel, which mixes with the air. These devices create fuel-air mixtures in differing proportions to fit the vehicle’s needs. They can also store and maintain the car’s fuel supply.
Spark Plug
The engine’s spark plug is responsible for igniting the fuel mixture within the combustion chamber. Its design can withstand changing temperatures and pressure levels to function properly.
Combustion Chamber
As the name implies, the combustion chamber is the area where fuel combusts. The cylinder head, cylinder walls, and piston surround the combustion chamber to prevent leaking. This crucial car engine part typically consists of aluminum because of its ability to squander heat.
Timing belts feature a rubber band material with teeth on the inside to coordinate the valve’s operation. Once a crankshaft turns, it triggers the timing belt. From there, the belt turns the camshaft.
Fuel Tank
Whether your car runs on gasoline or diesel, the fuel needs to be stored somewhere to run properly. Your fuel tank makes this possible.
Certain cars will have different sizes of fuel tanks, which you can typically find in the lower middle or rear part of the car.
If you have spilled gasoline inside your car, then we might be able to help you getting rid of the smell.
Cooling And Exhaust System
Radiator
One of the most important car engine parts is the radiator. There is a tremendous amount of heat that engines produce. The radiator works as a cooling system to protect the engine from overheating, which can cause severe damage.
Water Pump
To prevent your car engine from overheating, it relies on a water pump to provide coolant throughout the system. Water pumps release coolant to various area’s within the engine and absorb heat.
Without a functioning water pump, your car can risk overheating, which can cause substantial and even irreversible damage to the engine. The three most common types of water pumps are:
- Mechanical water pumps
- Electrical water pumps
- Water circulating pumps
Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is crucial for the car’s functioning, although it is not located in the engine area like other parts.
Its main purpose is to reduce toxic gases and pollutants through a series of chemical and redox reactions. It controls your car’s exhaust emissions to turn harmful gases into safer alternatives like steam. You can find the catalytic converter underneath your car’s main structure.
Engine Performance Enhancement
Supercharger
A supercharger is a device that boosts pressure to get more power from your engine. With a supercharger in your car engine, you can reap the following advantages:
- Smoother combustion
- Reduce exhaust emissions
- Increase the vehicle’s power output
- Promote a better overall efficiency
Turbocharger
Turbochargers function similarly to superchargers. Turbochargers use energy from exhaust gases to create an outward force from a gas turbine compressor.
Auxiliary Engine Parts
Flywheel
Energy storage is the main purpose of a car’s flywheel. This engine part absorbs the energy it receives from the crankshaft and other pieces. It can hold this energy until the mechanical makeup needs a boost.
Oil Pan
Also known as the sump, the engine’s oil pan collects the lubricant. It is set beneath the crankcase with screws to keep it secure and prevent leaks. When it comes time to change the oil, mechanics, place a drain plug at the bottom of the sump in order to remove dirty oil.
Governor
The speed at which your engine runs is due to your car’s governor. This piece regulates the supply of fuel to either increase or decrease the engine speed accordingly.
Manifolds
Manifolds are pipes that carry both the air-fuel mixture and exhaust gases. There are two distinct types in every car engine: intake manifolds and exhaust manifolds.
Intake manifolds provide the air-fuel mixture into gas engines to combust. However, in diesel engines, this pipe only carries air for combustion. Exhaust manifolds remove harmful gases from the combustion chamber.
Conclusion
Every car engine has dozens of important parts. Each device plays a crucial role in helping a car run smoothly. With a greater understanding of these car engine parts, you can identify how each one contributes to your vehicle’s operation.

Garry is the happy owner of a funky 2018 Nissan Juke Ti-S AWD. After growing up around his family’s mechanics shop, he is passionate about bringing budget-friendly car care to every driver. Garry has a business degree and is a car enthusiast.