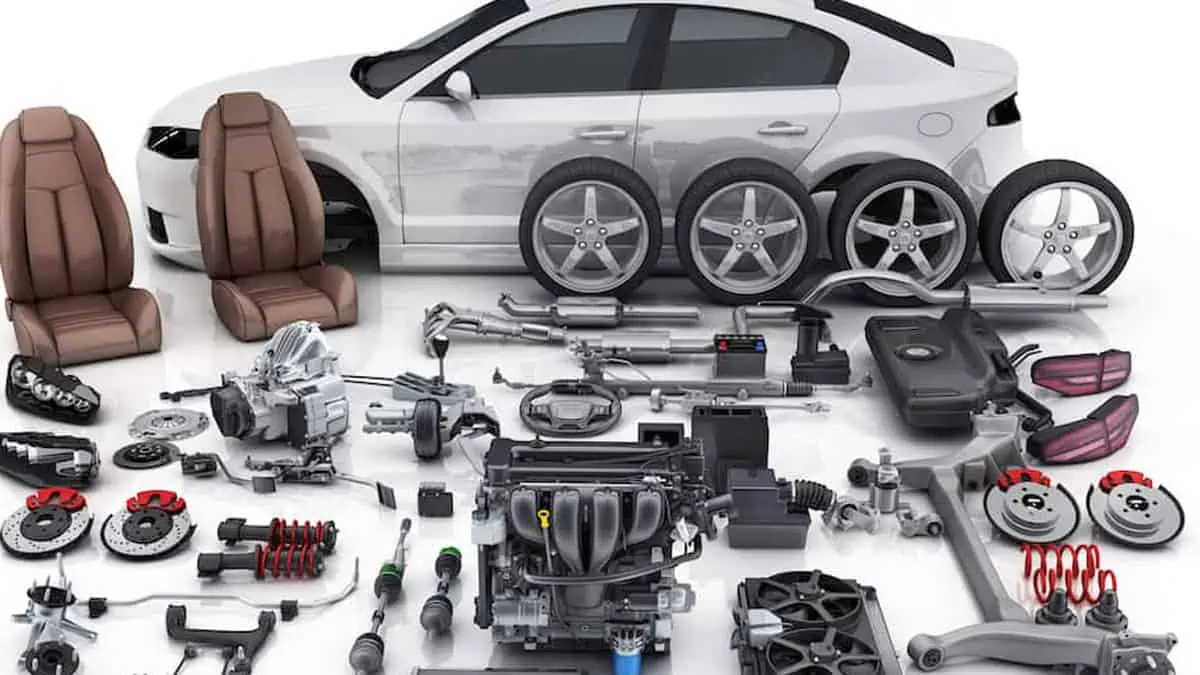
The best way to understand your car is to break it down to its fundamental components. Similar to a go-cart, your automobile essentially consists of an engine, a cooling system, a chassis, a steering wheel, four wheels, and a seat for the driver.
Current vehicle models have taken these fundamental parts to a new level, adding transmissions and convenience technology.
For some owners, knowing vehicle body parts might seem unnecessary. However, knowing the different car body part names and functions can offer several benefits.
For instance, understanding different car parts can go a long way in helping you maintain your vehicle correctly. Knowing each component’s role allows you to identify a problem early on and take the necessary steps to resolve it.
Learning your car’s body part names can also offer benefits such as:
- A better understanding of your car’s value
- Safer driving
- Self-reliance for repairs, troubleshooting, and more
- Foundational knowledge for hiring professional vehicle repair services
To help you realize these benefits and more, we cover ten exterior and ten interior car body part names below, along with a summary of each part.
Exterior Car Body Part Names
1. Roof And Pillars
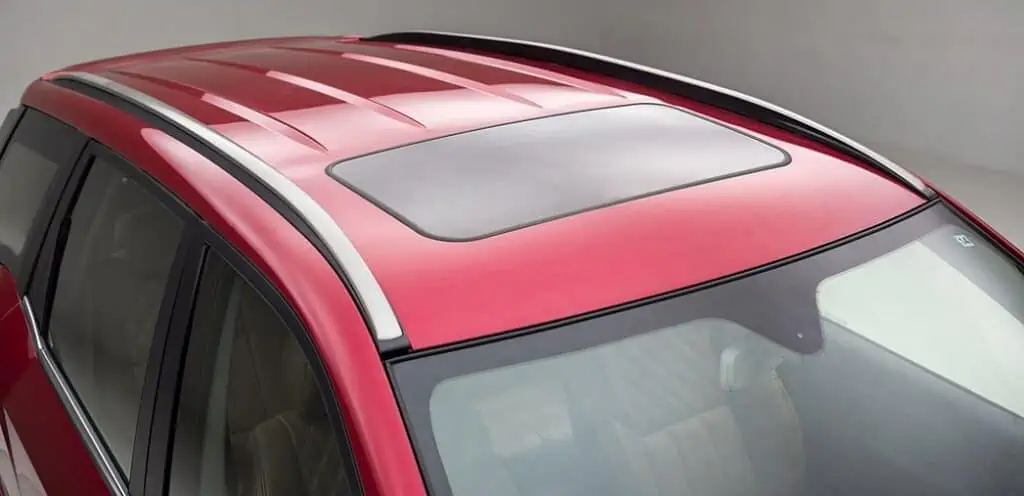

The roof is the top part of your car responsible for protecting you and your passengers from external elements. These come in many variations, depending on your vehicle’s make and model.
Pillars are the support beams that hold up your car’s roof. They also provide a significant amount of structural rigidity for the roof, windshield, and other upper frame parts. The number of pillars your vehicle has will depend on the vehicle’s length. Additionally, vehicle designs like the hatchback will have slanted pillars.
2. Hood
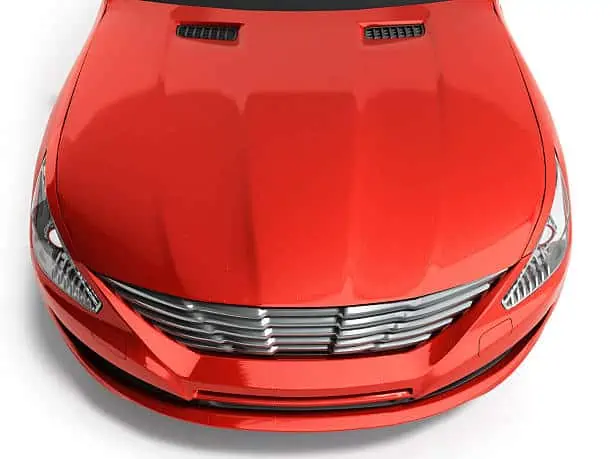

The hood is mainly located at the front of the vehicle, where the engine is. However, since the hood is placed on the same side as the engine, and some cars have their engines at the back, the hood’s position can change.
This car body part is responsible for protecting your vehicle’s engine and other related components from external elements like rain, dust, snow, and more. It also gives you the ability to access your car’s engine for potential repairs.
3. Trunk
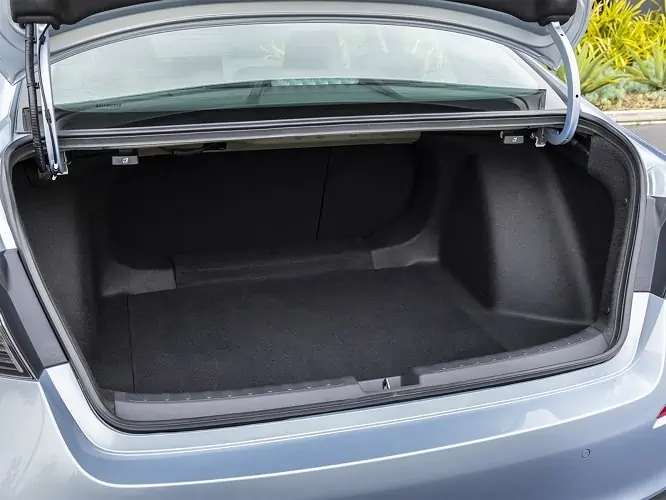

The trunk is the part of your car that allows you to store the belongings you carry with you, such as bags and luggage. All trunks come with a cover known as a lid, responsible for granting and denying people access.
In most cases, the trunk is located at the back of your vehicle. However, in cases where the engine is placed at the back, manufacturers will position the trunk at the front. Alternatively, in vehicle models that have the engine set in the middle, you will find trunks in the front and rear sides of the car.
4. Tires and Wheels
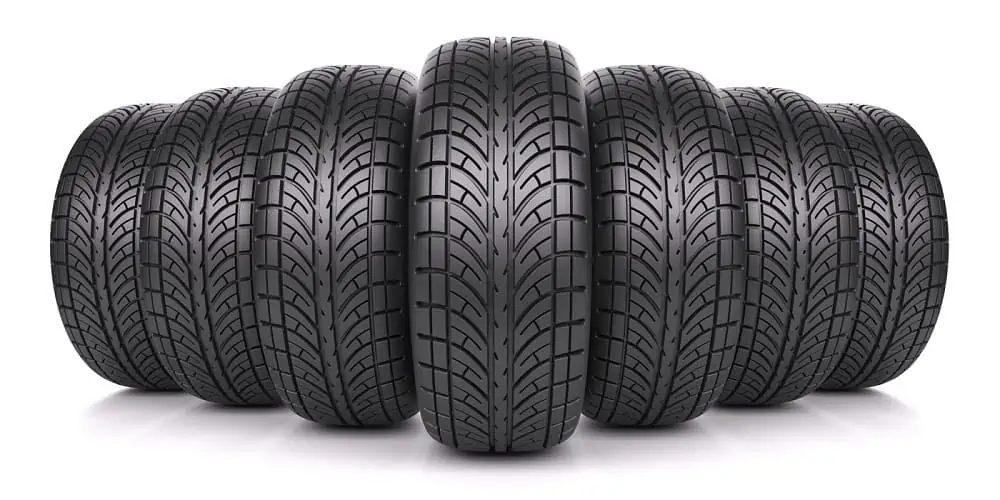

Tires are the ring-shaped parts of a car that act as the primary contact point of your vehicle and the terrain. Generally made from rubber, tires consist of a body and a tread layer. The body provides the necessary support, while the tread is a set of patterns responsible for giving the tire traction.
Found in the wheel cylinders, your vehicle’s wheels are the rims that hold the tire in place and often come in various sizes and styles.
5. Windshield
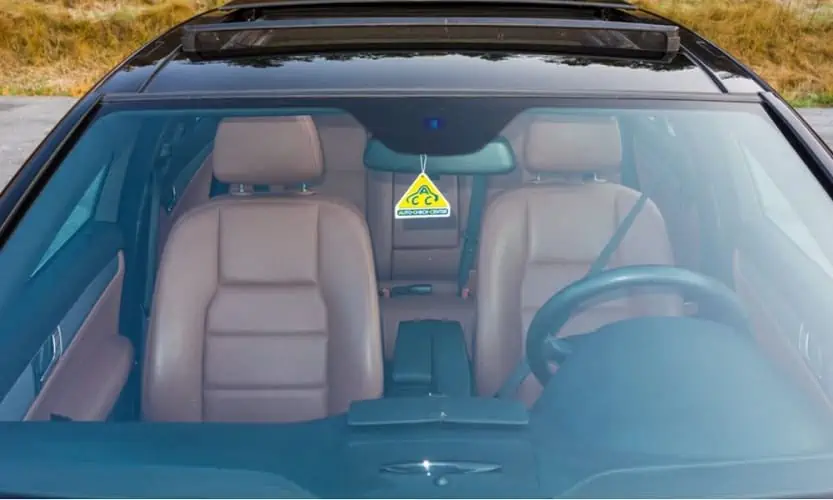

The windshield or windscreen is the glass at the front of the vehicle that allows you and your front-seat passenger to see the road. Its primary purpose is to protect you from external elements and the wind your car creates while moving forward at high speeds.
While it was initially made of a simple piece of glass, modern windshields are made using laminated safety glass to prevent broken pieces of glass from harming the vehicle’s occupants.
6. Doors And Windows
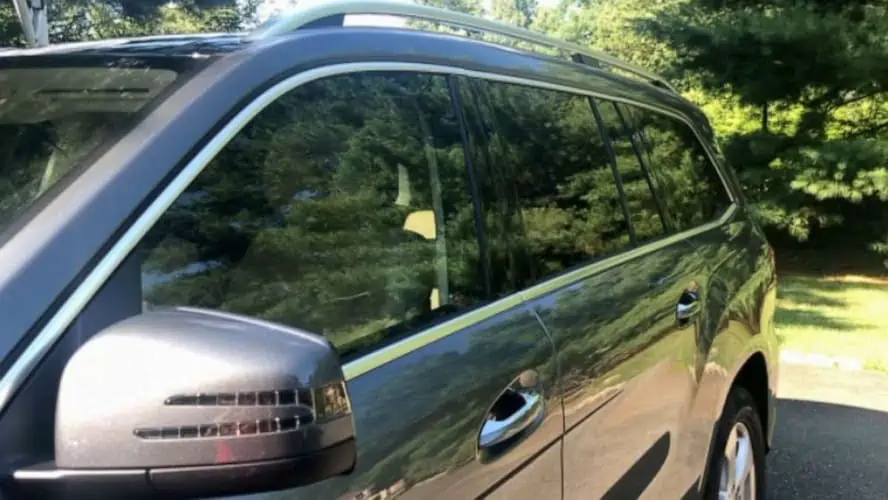

As far as car exterior parts go, doors and windows are straightforward. The doors are the parts of your vehicle that you open to get in and out of your car. They are also responsible for keeping you safe while driving.
Car doors have different parts, such as the door lock, panel, handle, and storage compartment. Your vehicle could have anywhere between two to four doors, depending on its model. Also, while you can open most doors manually, it is not uncommon to have car doors that you can control from a distance.
Doors also serve as mounts for the windows, responsible for protecting you against external elements. However, unlike the windshield, you can roll these windows up and down using the window glass controller that you will find in the door.
7. Grille

Usually, a significant style component of your car and probably one of the first things you look at, the grille is the part of your car that covers the opening found at the front. Besides enabling air to enter and exit, these parts of your vehicle also serve to protect the radiator and engine.
8. Front And Rear Bumper
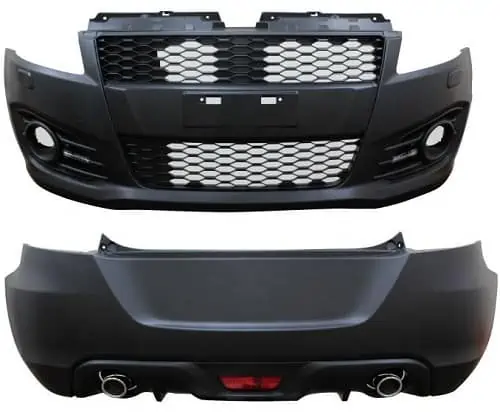

The bumper is an exterior part of your car attached to the front and rear ends. It is mainly responsible for keeping your car’s body parts safe from collisions and minor bumps.
Though they were made using metal in the past, modern bumpers are made of various materials, from aluminum and plastic to carbon fiber. The materials used in these parts go a long way in ensuring the bumper absorbs the shock created during crashes.
Besides limiting the physical damages your car experiences, front and rear bumpers also help enhance your vehicle’s appearance. As such, it is common to find different types of stylish bumpers, including:
- Cowboy bumpers
- Tube bumpers
- Standard bumpers
- Step bumpers
9. Head And Tail Lights

Also referred to as a headlamp, the headlight is positioned at the front of your car and is responsible for providing you with visibility when driving at night. You can set your headlights to different modes, each producing varying types of light, including full-beam light, fog light, dipped light, and more.

Taillights, also called tail lamps, are the cluster of lights found at the rear of your car. They make your vehicle visible to the motorists behind. For instance, brake lights notify other drivers that you are slowing down or coming to a complete stop. Doing so helps you prevent other vehicles from hitting your car from behind.
There are currently several types of head and tail lights, including halogens, laser, HIDs, and LEDs. However, LEDs are more popular because of their energy efficiency. On top of that, they are also brighter than most other types of bulbs.
10. Signal Lights

Signal lights are a collection of lights found at the front and rear of your car that blinks when switched on. They are responsible for informing other motorists of the direction you intend to head towards. Usually, the controls for signal lights are found on the left of your steering wheel column if you have a right-hand drive vehicle.
New cars have front and back turning signals and emergency lights that work by blinking all turning signals at once to increase your car’s visibility.
Interior Car Body Part Names
1. Engine
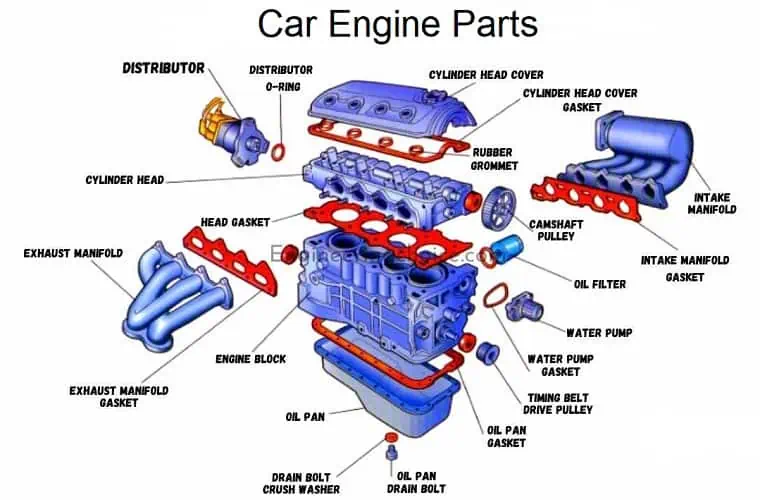
The engine is considered the heart of your car. It creates the force needed to turn your vehicle’s wheels, propelling it forward, achieving this by converting the heat from burning gas.
Though this sounds simple, the task the engine performs is actually quite complex. It needs to be strong enough to handle the immense load. Fortunately, many types of engines are available, each featuring different structures that determine how efficient they function. Additionally, drivers have the option of modifying their engine’s performance further.
Brief Summary Of Your Engine’s Auto Parts
To give you a better understanding of how your vehicle’s engine functions, here is a summary of some of its parts, along with the role they play.
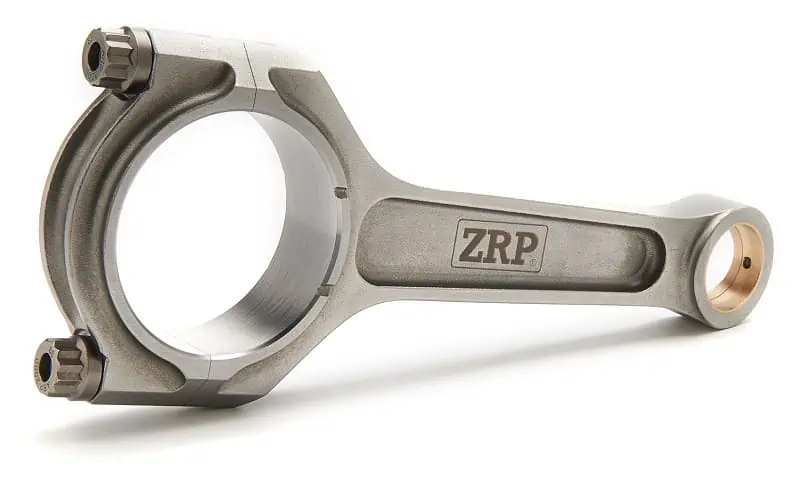

Connecting Rod: This is the part of the engine attached to a piston, which in turn connects it to the crankshaft responsible for rotating the latter.

Pistons: In most internal combustion engines, pistons are responsible for compressing air and gas inside a cylinder, pushing them down to drive the engine’s crankshaft via the connecting rod.

Crankshaft: Attached to the pistons through the connecting rod and connected to the flywheel, the crankshaft utilizes rod bearings to rotate.
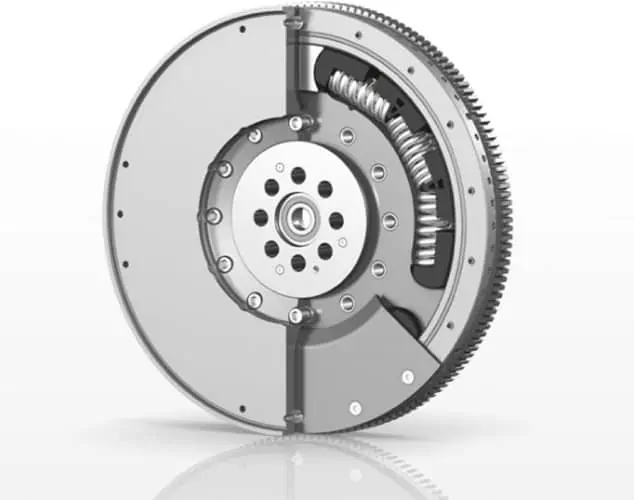

Flywheel: This device is responsible for storing rotational energy, providing power transfer between your vehicle’s engine and its transmission. The rotational energy the flywheel offers is essential in keeping the engine running. If that wasn’t enough, the flywheel is also responsible for switching the engine on via the starter ring.
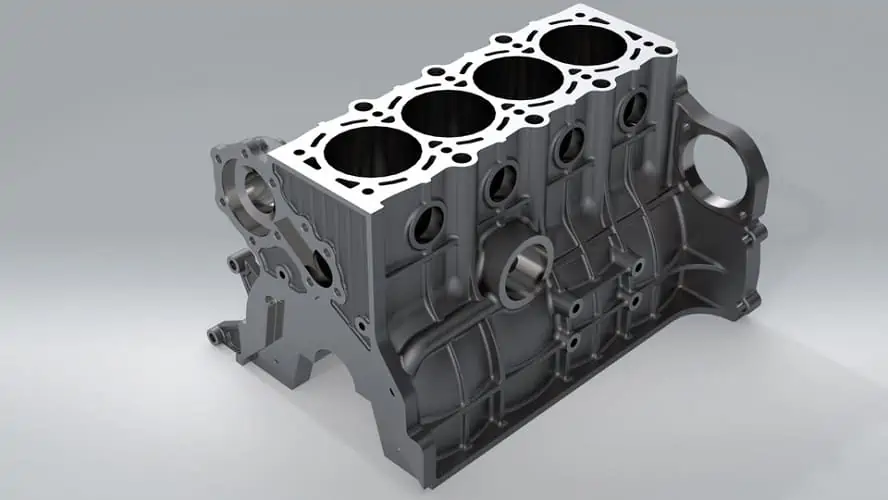

Cylinder and Cylinder Head: The cylinder is the space in which the pistons travel. Cylinder heads (heads) are found on top of the cylinder block. Their primary role is to close the cylinder and keep the pressure contained in the combustion chamber.
Usually, this is where you will find the spark plugs, valves, and fuel injectors mounted. As the fuel injectors spray fuel into the combustion chamber, the spark plugs deliver the spark that burns the air/fuel mix. The valves, meanwhile, are responsible for controlling the air/fuel mix flow.

Camshaft: A cam is a teardrop-shaped object responsible for opening the valves at different times during the combustion process. The camshaft is what the cam is mounted on.
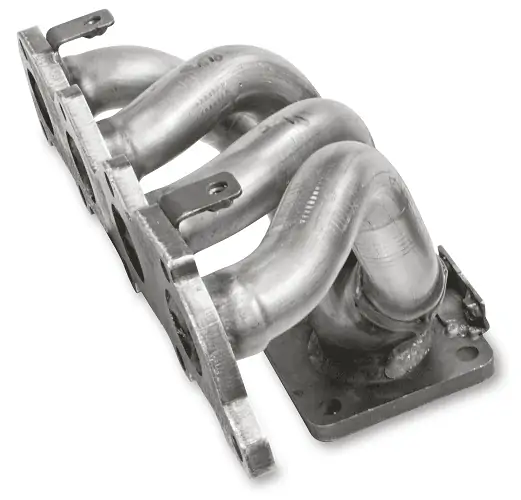

Intake and Exhaust Manifold: Also known as the inlet manifold, the intake manifold is the part of the engine responsible for supplying the air/fuel mixture to the engine’s cylinders. On the other hand, the exhaust manifold’s main job is to collect the exhaust gasses from the multiple cylinders that internal combustion engines have, guiding these gasses to a single pipe.
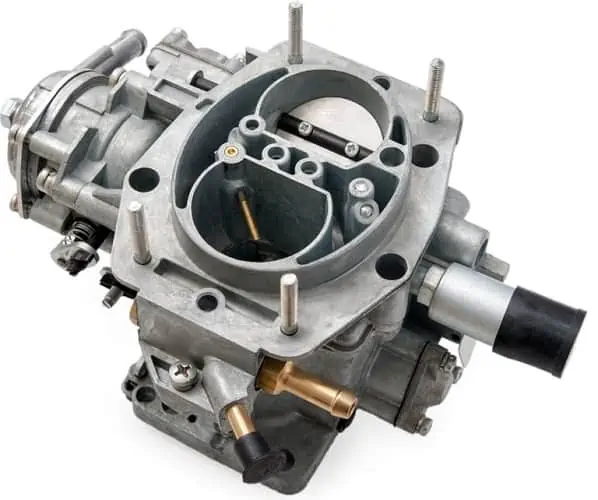

Carburetor: Though most modern engines do not have this part since they use fuel injection, the engines in older vehicle models come with a carburetor, a component responsible for mixing the fuel and air.
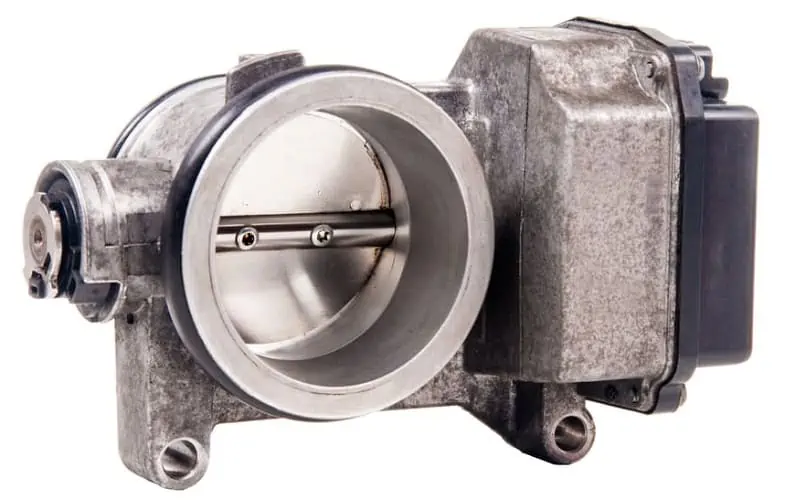

Throttle Body: While modern engines lack carburetors, they have a throttle body that controls the amount of air that goes into the engine. In doing so, the part controls how much fuel the engine burns. You can directly control the throttle body using the car’s accelerator or throttle pedal.
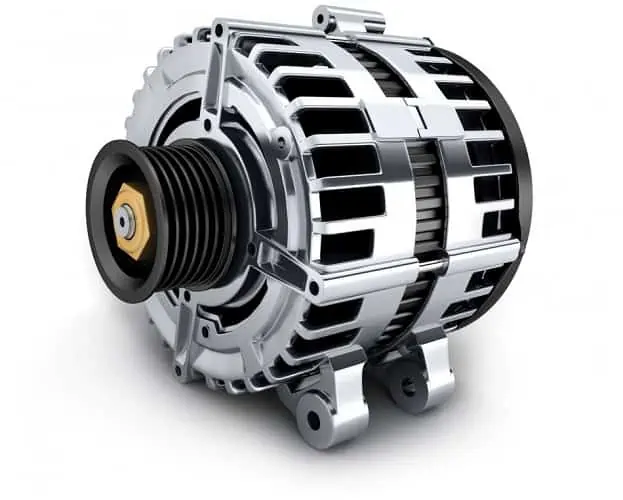

2. Alternator
The alternator is an essential part of your vehicle. Though most people credit the battery for powering the car’s electrical parts, the alternator is the primary component behind this functionality.
Alternators are often placed in front or beside your vehicle’s engine since that is where it gets its mechanical power from. They are responsible for generating the electric power that charges the battery while the engine is running. It also supplies this electrical power to certain vehicle mechanisms.
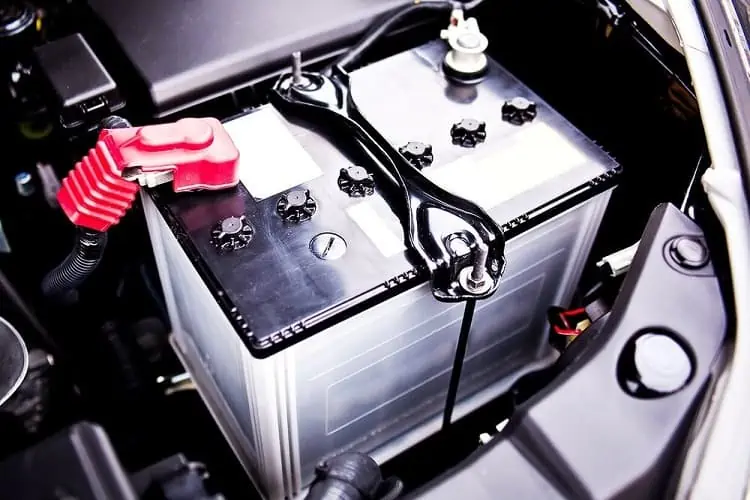

3. Battery
Your battery is another vital part your vehicle needs to run, enabling all your vehicle’s electrical components to function correctly.
In the past, most components in a car were manual, making batteries pointless. However, modern technology has made them crucial.
Modern batteries don’t have a very complex structure. Most are simply wet cell batteries with six cells. However, various types of batteries are available, each type offering unique advantages.

4. Radiator
With your radiator responsible for keeping your engine cool when it is running, it goes a long way in ensuring your vehicle is operating efficiently. A malfunctioning radiator can result in a damaged engine due to overheating.
The radiator consists of several essential parts, including the transmission cooler, core, pressure cap, inlet, and outlet tank. These parts work to keep your engine cool by absorbing the heat from the liquid and gas that enter the engine. The heat the radiator absorbs is then sent outside the vehicle.

5. Muffler
The muffler is a part of your car’s exhaust system positioned at the rear bottom of your vehicle to reduce engine noise and dampen emissions.
While its functionality is straightforward, the science behind it can be a bit complex. When the exhaust valve opens, it releases burnt gasses into the exhaust system. These burnt gasses create a powerful sound wave which the muffler lowers before releasing it outside.
Most mufflers are often made using steel with aluminum coating, making them strong enough to withstand vast amounts of heat.
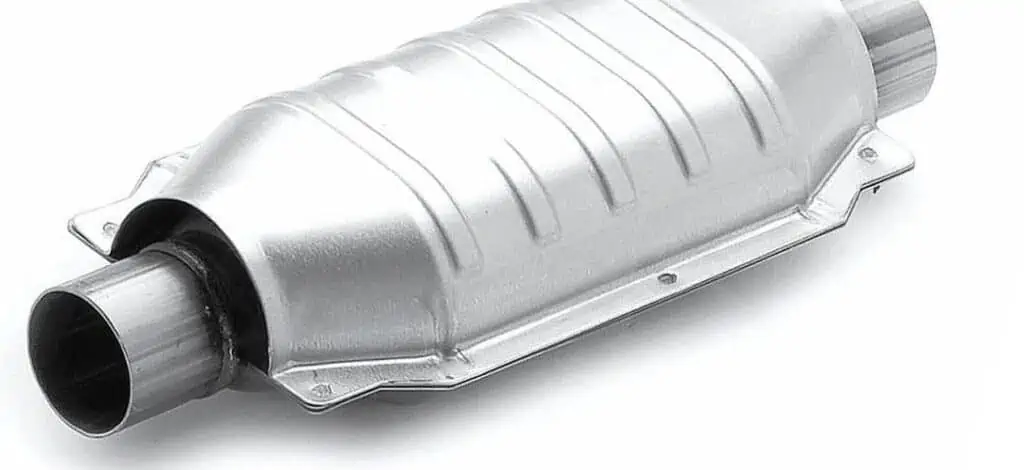

6. Catalytic Converter
Due to the engine process, your vehicle’s exhaust gas contains nitrogen dioxide, carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitric oxide. The catalytic converter uses chemical processes to convert these emissions into water vapor and carbon dioxide.
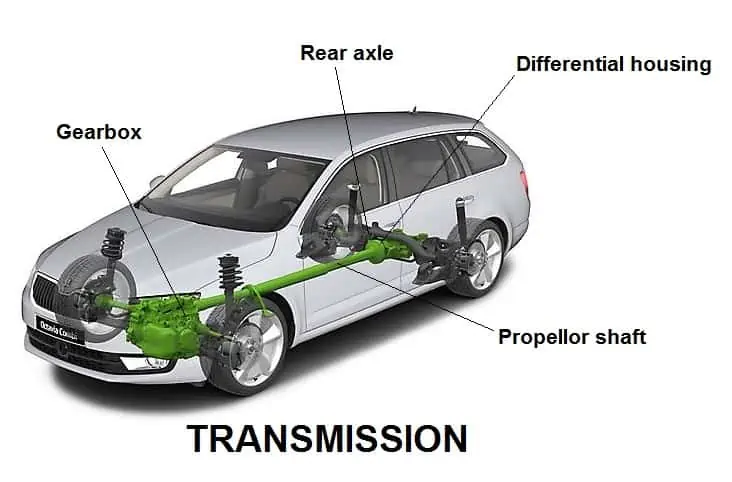
7. Transmission
Your vehicle’s transmission refers to its gearbox. However, some consider the term transmission a broader concept encompassing the entire drive train, including the clutch, gearbox, prop shaft, differential, and final drive shaft.
The transmission helps you change your speed and torque with the help of gears and gear trains. It comes with a few gear ratios that enable you to switch between them, depending on the speed variation.
Also, while shifting between gears had to be done manually in previous vehicle models, more and more vehicles today come fitted with automatic transmissions.
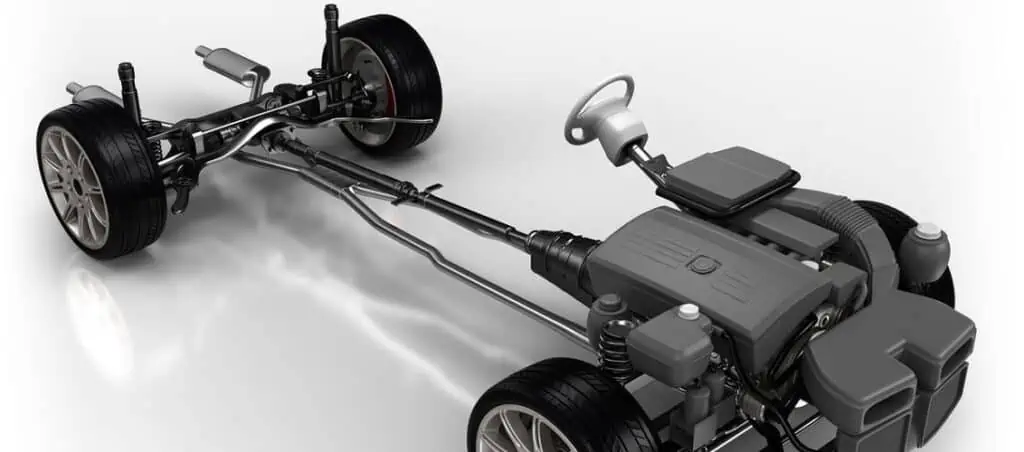

8. Axle
The axle is a shaft found underneath your car. It holds the wheels together, enabling them to rotate accordingly. The part also plays a role in carrying the weight of your vehicle.
There are three major types of axles, namely the front axle, rear axle, and stub axle. The front axle keeps your vehicle’s front wheel together while the rear axle joins the rear wheels. The stub axle is responsible for connecting the central axle and the wheels.
The number of axles your car has depends on its size. However, in most cases, the front axle is responsible for responding to the steering wheel’s movements.
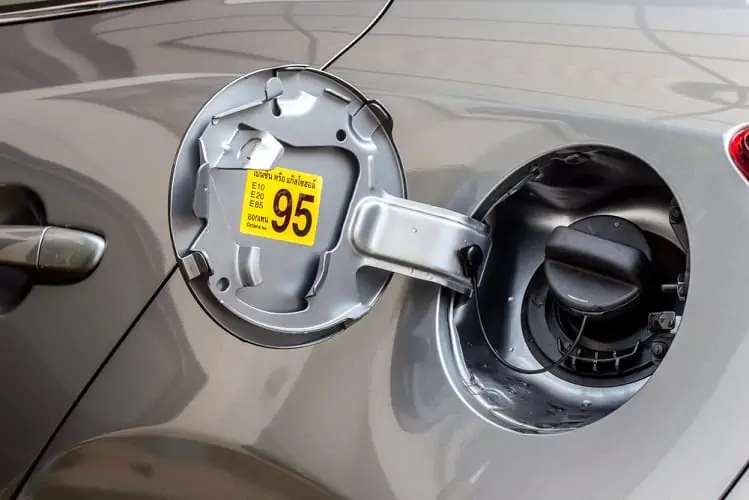

9. Fuel Tank
The fuel tank is the storage space for the fuel that helps your vehicle run. Fuel tanks come with an opening through which fuel is inserted. They also have an opening that guides the fuel to the engine.
The size of the tank will vary depending on the size of your car. For instance, compact cars have smaller fuel tanks than other cars. In order to avoid contaminating the fuel, fuel tanks are generally made using a combination of different materials. Doing so also makes the tanks rustproof, further protecting the fuel.
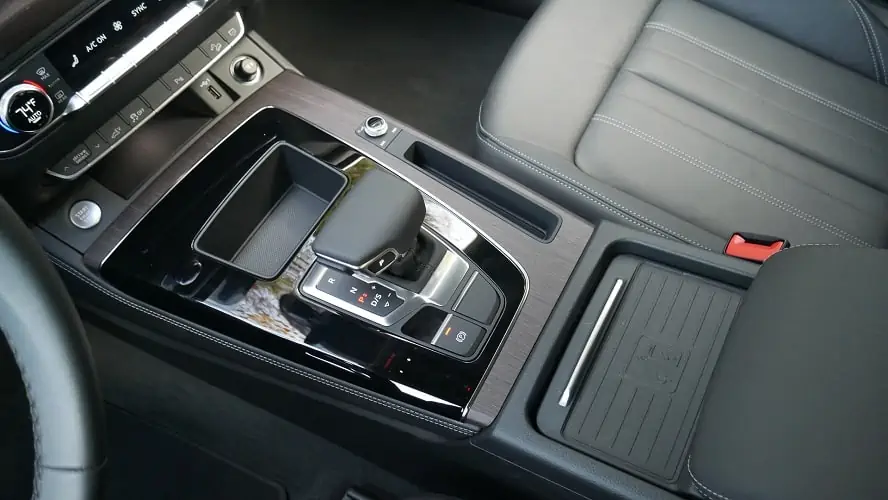

10. Center Console
Your vehicle’s center console is mounted on top of the transmission tunnel, which runs between your vehicle’s centerline. It is where the dashboard begins and is also the standard position of the gear shifter. Center consoles can vary greatly, depending on the vehicle’s make and model. Some center consoles have cubby holes and cup holders, while others control comfort devices and onboard entertainment.
Conclusion
The exterior and interior car body part names above are only a few of the common areas you need to know. Though the descriptions we have offered are brief and straightforward, doing more research could prove additionally beneficial.

Garry is the happy owner of a funky 2018 Nissan Juke Ti-S AWD. After growing up around his family’s mechanics shop, he is passionate about bringing budget-friendly car care to every driver. Garry has a business degree and is a car enthusiast.

